Key Takeaways
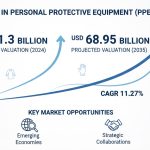
- The global Anticoccidial Drugs Market is projected to grow from USD 184.3 million in 2023 to USD 268.1 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 4.3%.
- Market growth is driven by rising livestock production, increasing prevalence of coccidiosis, and advancements in drug development.
- Ionophore and synthetic drugs dominate the market, with ongoing innovation in both segments.
- Coccidiostatic and coccidiocidal drugs offer different mechanisms of action, influencing treatment strategies and market trends.
- Livestock remains the primary consumer segment, but companion animal applications are rising.
- North America leads the market, while Asia-Pacific presents significant growth opportunities.
- Key players are focusing on partnerships, acquisitions, and R&D to maintain competitiveness.
- Future trends include novel drug formulations, increased regulatory scrutiny, and growing consumer awareness.
Anticoccidial Drugs Market Overview
The global Anticoccidial Drugs Market is experiencing robust growth, reflecting the increasing need for effective management of coccidiosis—a parasitic disease that significantly impacts animal health and agricultural productivity. According to Vantage Market Research, the market was valued at USD 184.3 million in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 268.1 million by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2024 to 2032. This growth trajectory is underpinned by several key factors, including the rising demand for animal protein, expansion of the livestock industry, and heightened awareness of animal health and welfare.
One of the primary drivers of market expansion is the increasing prevalence of coccidiosis, particularly in poultry and livestock. Coccidiosis can cause significant economic losses due to reduced productivity, increased mortality, and higher veterinary costs. As a result, there is a growing emphasis on preventive healthcare and the adoption of anticoccidial drugs to safeguard animal health and ensure food security. Additionally, the intensification of animal farming practices, especially in emerging economies, has led to higher disease transmission rates, further fueling the demand for effective anticoccidial solutions.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a mixed impact on the anticoccidial drugs market. While initial disruptions in supply chains and reduced veterinary visits temporarily hampered market growth, the pandemic also underscored the importance of biosecurity and disease prevention in animal husbandry. As the world recovers, the market is witnessing renewed investments in animal health infrastructure and a surge in demand for veterinary pharmaceuticals, including anticoccidial drugs.
Moreover, technological advancements in drug formulation and delivery methods are enhancing the efficacy and safety profiles of anticoccidial drugs. The integration of digital tools for disease monitoring and management is also contributing to market growth by enabling timely interventions and optimizing drug usage. Overall, the anticoccidial drugs market is poised for sustained expansion, driven by a confluence of demographic, economic, and technological factors.
Drug Class Segmentation
The anticoccidial drugs market is broadly segmented into two main classes: ionophores and synthetic drugs. Each class has distinct characteristics, mechanisms of action, and market dynamics, shaping the competitive landscape and influencing treatment protocols across different animal species.
Ionophores are naturally derived compounds that disrupt the ionic balance within coccidian parasites, leading to their death. They are widely used in poultry and livestock due to their efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and ability to prevent the development of resistance when used in rotation with other drug classes. Ionophores, such as monensin and salinomycin, account for a significant share of the market, particularly in regions with intensive animal farming practices.
Synthetic drugs, on the other hand, are chemically synthesized compounds that target specific stages of the coccidian life cycle. These include sulfonamides, amprolium, and toltrazuril, among others. Synthetic drugs are often preferred in cases where resistance to ionophores has developed or when a rapid therapeutic response is required. The market share of synthetic drugs is growing, driven by ongoing research and development efforts aimed at enhancing their efficacy, safety, and spectrum of activity.
Market share insights reveal that ionophores currently dominate the global market, particularly in North America and Europe, where regulatory frameworks support their use in animal feed. However, the synthetic segment is gaining traction, especially in regions with stringent regulations on antibiotic use and rising concerns about drug residues in animal products.
Trends in drug development are increasingly focused on combination therapies, novel delivery systems, and the development of next-generation molecules with improved resistance profiles. The push for sustainable and residue-free animal production is also driving innovation in both ionophore and synthetic drug segments, with companies investing in research to develop safer and more effective anticoccidial solutions.
Action Types of Anticoccidial Drugs
Anticoccidial drugs are classified based on their mode of action into two main categories: coccidiostatic and coccidiocidal agents. Understanding the differences between these action types is crucial for optimizing treatment strategies and managing resistance.
Coccidiostatic drugs inhibit the growth and reproduction of coccidian parasites, effectively controlling the infection without necessarily killing the organisms outright. This approach allows the host’s immune system to mount a response and develop immunity over time. Coccidiostatic agents are commonly used in preventive programs, particularly in large-scale poultry and livestock operations where continuous exposure to low levels of the parasite is expected.
Coccidiocidal drugs, in contrast, are designed to kill the parasites directly, providing a rapid and decisive response to acute infections. These drugs are often employed in therapeutic settings where immediate parasite clearance is necessary to prevent severe disease and mortality. The choice between coccidiostatic and coccidiocidal agents depends on several factors, including the severity of the infection, the species affected, and the risk of resistance development.
Growth trends in drug action segments indicate a rising preference for coccidiocidal agents in high-value animal production systems, where rapid recovery and minimal production losses are critical. However, coccidiostatic drugs remain the mainstay of preventive programs due to their cost-effectiveness and lower risk of resistance when used appropriately.
Research and development contributions are focused on identifying new molecular targets, improving drug delivery, and minimizing adverse effects. Advances in molecular biology and genomics are enabling the discovery of novel compounds with unique mechanisms of action, offering hope for overcoming the challenge of drug resistance. Additionally, the integration of immunomodulatory agents and vaccines with traditional anticoccidial drugs is emerging as a promising strategy for comprehensive coccidiosis control.
Animal Type Insights
The application of anticoccidial drugs spans a wide range of animal species, with distinct market dynamics and growth potential in each segment. The two primary categories are companion animals and livestock, each presenting unique challenges and opportunities for market players.
Livestock, including poultry, cattle, sheep, and swine, represent the largest consumer segment for anticoccidial drugs. The high prevalence of coccidiosis in intensive farming systems, coupled with the economic impact of the disease, drives substantial demand for preventive and therapeutic interventions. Poultry, in particular, accounts for the majority of anticoccidial drug usage, given the susceptibility of broilers and layers to Eimeria infections and the scale of global poultry production.
Companion animals, such as dogs and cats, are also susceptible to coccidiosis, albeit to a lesser extent than livestock. The rising trend of pet ownership, increased spending on veterinary care, and growing awareness of zoonotic diseases are contributing to the expansion of the companion animal segment. While the market share remains smaller compared to livestock, the segment offers significant growth potential, especially in developed regions with high pet ownership rates.
The prevalence of coccidiosis varies across species and geographies, influenced by factors such as climate, farming practices, and biosecurity measures. In regions with intensive animal husbandry and limited access to veterinary services, the burden of coccidiosis is particularly high, underscoring the need for accessible and affordable anticoccidial solutions.
Growth potential in animal segments is further supported by the increasing adoption of integrated disease management programs, combining anticoccidial drugs with improved hygiene, nutrition, and vaccination. As the global demand for animal protein continues to rise, ensuring the health and productivity of livestock through effective coccidiosis control will remain a top priority for producers and policymakers alike.
Regional Market Analysis
The global anticoccidial drugs market exhibits significant regional variation, shaped by differences in animal production systems, regulatory environments, and disease prevalence. North America currently dominates the market, driven by advanced veterinary infrastructure, high levels of animal protein consumption, and robust regulatory frameworks supporting the use of anticoccidial drugs.
In North America, the United States is the largest market, benefiting from a well-established livestock industry, extensive research and development activities, and a strong focus on animal health and welfare. The presence of leading pharmaceutical companies and a favorable reimbursement landscape further contribute to the region’s market leadership.
Europe is another key market, characterized by stringent regulations on antibiotic use and a growing emphasis on sustainable animal production. The European Union’s ban on antibiotic growth promoters has accelerated the adoption of alternative anticoccidial strategies, including vaccines and non-antibiotic drugs. This regulatory shift is driving innovation and creating opportunities for market players to develop novel solutions that meet evolving consumer and regulatory demands.
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region, fueled by rapid urbanization, rising incomes, and increasing demand for animal protein. Countries such as China, India, and Brazil are witnessing significant investments in livestock production, creating a fertile ground for the expansion of the anticoccidial drugs market. However, challenges such as limited access to veterinary services and variable regulatory standards may hinder market growth in some areas.
The competitive landscape across regions is marked by the presence of both multinational corporations and local players, each vying for market share through product innovation, strategic partnerships, and geographic expansion. As the market continues to evolve, companies that can navigate regional complexities and adapt to local needs will be best positioned for success.
Key Players in the Market
The anticoccidial drugs market is highly competitive, with a mix of established pharmaceutical giants and emerging players driving innovation and market growth. Leading companies such as Zoetis Inc., Elanco Animal Health, Merck & Co., Ceva Santé Animale, and Boehringer Ingelheim have established strong footholds through extensive product portfolios, global distribution networks, and ongoing investments in research and development.
Recent strategic initiatives by key players include mergers and acquisitions, partnerships with research institutions, and the launch of new products targeting emerging disease threats. For example, Zoetis has expanded its portfolio through the acquisition of complementary businesses and the development of next-generation anticoccidial drugs. Elanco has focused on strategic collaborations to enhance its R&D capabilities and accelerate the commercialization of innovative solutions.
The importance of partnerships and acquisitions cannot be overstated in this dynamic market. Collaborations between pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, and government agencies are facilitating the development of novel drug candidates, improving access to veterinary care, and supporting the implementation of integrated disease management programs. These strategic alliances are also enabling companies to navigate regulatory challenges, expand their geographic reach, and respond to evolving market demands.
In addition to established players, a growing number of startups and biotech firms are entering the market, leveraging advances in molecular biology, genomics, and digital health to develop cutting-edge anticoccidial solutions. As competition intensifies, companies that can combine scientific excellence with commercial acumen will be well-positioned to capture a share of the growing anticoccidial drugs market.
Future Trends and Opportunities
The future of the anticoccidial drugs market is shaped by a confluence of technological innovation, changing consumer preferences, and evolving regulatory landscapes. One of the most significant trends is the development of novel drug formulations that offer improved efficacy, safety, and ease of administration. Advances in nanotechnology, sustained-release delivery systems, and combination therapies are enabling more targeted and effective coccidiosis control, reducing the risk of resistance and minimizing environmental impact.
Rising consumer awareness and health spending are also driving demand for high-quality, residue-free animal products. As consumers become more conscious of food safety and animal welfare, producers are under increasing pressure to adopt sustainable and transparent production practices. This shift is creating opportunities for the development of non-antibiotic anticoccidial solutions, such as vaccines, probiotics, and phytogenic additives, which align with the growing demand for natural and organic products.
Potential regulatory impacts on market growth are another key consideration. Governments and regulatory agencies are implementing stricter guidelines on the use of veterinary pharmaceuticals, particularly antibiotics, to combat the rise of antimicrobial resistance. While these regulations present challenges for market players, they also create opportunities for innovation and differentiation. Companies that can develop compliant, effective, and sustainable anticoccidial solutions will be well-positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape.
Looking ahead, the integration of digital technologies, such as precision livestock farming and real-time disease monitoring, is expected to revolutionize coccidiosis management. These tools enable early detection, targeted treatment, and data-driven decision-making, enhancing the overall effectiveness of anticoccidial programs. As the market continues to evolve, stakeholders across the value chain must embrace innovation, collaboration, and adaptability to capitalize on emerging opportunities and address the complex challenges of coccidiosis control.
☎ Contact Us:
224 W 35th St Ste 500 New York,
USA/Canada Toll Free +1(877) 462-2282
+1(212) 951-1369
✉ Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://www.vantagemarketresearch.com
FAQs
- What factors are driving the growth of the Anticoccidial Drugs Market?
- How is the Anticoccidial Drugs Market expected to evolve by 2032?
- What is the significance of the projected CAGR of 4.3% from 2024 to 2032 in the Anticoccidial Drugs Market?
- What is the current market valuation of the Anticoccidial Drugs Market in 2023?
![[Market Research Reports] – Research Google News Blog | VMR.Biz](https://www.vmr.biz/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/logo-removebg-preview.png)