The Rise of Micro Irrigation Systems: Transforming Global Agriculture Through Water-Efficient Technology
Key Takeaways
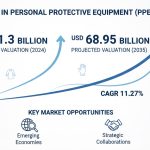
- The global micro irrigation systems market reached USD 10,260.17 million in 2022 and is projected to grow to USD 20,444.05 million by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.00% during the forecast period.
- Drip irrigation systems dominate the market segment, accounting for the largest share due to their superior water efficiency and precise nutrient delivery capabilities, making them ideal for high-value crops and water-scarce regions.
- The agriculture sector remains the primary end-user of micro irrigation systems, with orchard crops and greenhouse cultivation driving significant adoption rates as farmers seek to maximize yields while minimizing water consumption.
- Asia Pacific emerges as the fastest-growing regional market, driven by government initiatives promoting water conservation, increasing agricultural mechanization, and rising awareness about sustainable farming practices among smallholder farmers.
- Technological innovations including smart sensors, IoT integration, and automated fertigation systems are revolutionizing the micro irrigation landscape, enabling farmers to achieve unprecedented levels of precision in water and nutrient management.
Market Overview
The Micro Irrigation Systems Market stands at a pivotal juncture in 2023, experiencing unprecedented growth driven by the global imperative to address water scarcity and enhance agricultural productivity. With the market valued at approximately USD 11,200 million in 2023, the trajectory toward the projected USD 20,444.05 million by 2030 reflects not just numerical growth but a fundamental shift in how the world approaches agricultural water management. This remarkable expansion is underpinned by several converging factors that make micro irrigation not just an option but a necessity for modern agriculture.
Climate change has intensified the urgency for water-efficient farming practices, with many regions experiencing more frequent droughts and unpredictable rainfall patterns. Traditional flood irrigation methods, which can waste up to 50% of water through evaporation and runoff, are becoming increasingly unsustainable. In contrast, micro irrigation systems deliver water directly to plant roots, achieving efficiency rates of 90% or higher. This efficiency translates directly into economic benefits for farmers, who can reduce water costs while maintaining or even increasing crop yields.
Government policies worldwide are accelerating market growth through subsidies, grants, and regulatory frameworks that incentivize the adoption of water-saving technologies. Countries like India, Israel, and the United States have implemented comprehensive programs that provide financial assistance to farmers transitioning to micro irrigation systems. These initiatives recognize that water security is intrinsically linked to food security, making investment in efficient irrigation infrastructure a national priority.
The market faces several challenges that temper its growth potential. High initial installation costs remain a significant barrier, particularly for small-scale farmers in developing countries. A typical drip irrigation system can cost between 1,000to1,000to3,000 per hectare, depending on the crop type and terrain complexity. Additionally, the need for technical expertise in system design, installation, and maintenance creates adoption hurdles in regions with limited agricultural extension services. Clogging of emitters due to water quality issues and the environmental concerns related to plastic waste from irrigation components also pose ongoing challenges that the industry must address through innovation and sustainable practices.
Types of Micro Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation systems have emerged as the undisputed leader in the micro irrigation market, commanding over 60% of the total market share. This dominance stems from their unparalleled precision in water delivery and versatility across diverse crop types and terrains. Modern drip systems utilize a network of pipes, tubes, valves, and emitters to deliver water drop by drop directly to the plant root zone. This targeted approach minimizes water loss through evaporation and prevents weed growth between crop rows, as only the immediate vicinity of the plant receives moisture.
The technology behind drip irrigation has evolved significantly, with pressure-compensating emitters now standard in most commercial installations. These advanced emitters ensure uniform water distribution even on sloping terrain or over long lateral lines, addressing one of the historical limitations of early drip systems. Subsurface drip irrigation (SDI) represents the latest evolution, where drip lines are buried below the soil surface, further reducing evaporation losses and protecting the infrastructure from damage by farm machinery or UV degradation.
Sprinkler irrigation systems constitute the second-largest segment, particularly popular for crops that benefit from overhead water application. Micro-sprinklers and mini-sprinklers offer a middle ground between traditional overhead irrigation and drip systems, providing localized water application with slightly larger wetted areas than drip emitters. These systems excel in orchard applications where tree canopy coverage and root spread require broader water distribution patterns. The ability to provide frost protection through overhead sprinkling adds another dimension to their utility, making them indispensable in regions prone to late spring frosts.
When comparing effectiveness between drip and sprinkler systems, the choice often depends on specific crop requirements, soil characteristics, and water quality. Drip irrigation typically achieves 90-95% application efficiency compared to 75-85% for micro-sprinklers. However, sprinkler systems offer advantages in terms of lower filtration requirements and easier visual inspection of system operation. For salt-sensitive crops, drip irrigation’s ability to maintain a low-salinity zone around the root system provides a crucial advantage. Conversely, sprinkler systems better suit closely spaced crops like alfalfa or certain vegetables where the cost of installing drip lines for each row becomes prohibitive.
Agriculture Segment Insights
Agriculture remains the cornerstone of micro irrigation system deployment, accounting for over 85% of global market consumption. Within this vast sector, the application patterns reveal fascinating insights into how different crop categories drive technology adoption. Row crops, including cotton, sugarcane, and corn, have witnessed exponential growth in micro irrigation adoption, particularly in regions where water rights are becoming increasingly restricted. The ability to apply water and fertilizers with surgical precision has transformed the economics of these traditionally flood-irrigated crops.
Orchard crops represent a particularly significant segment, with nearly 70% of new orchard plantings worldwide incorporating micro irrigation from establishment. The perennial nature of fruit trees and their high value per unit area make them ideal candidates for the capital investment required by micro irrigation systems. Citrus groves in Mediterranean climates, almond orchards in California, and apple plantations in water-scarce regions have demonstrated yield improvements of 20-40% when converting from traditional irrigation methods. The ability to manage water stress precisely during critical phenological stages, such as fruit sizing and sugar accumulation, has revolutionized orchard management practices.
The shift towards greenhouse cultivation marks another transformative trend in agricultural micro irrigation adoption. Protected agriculture environments demand precise control over all growing parameters, making micro irrigation systems not just beneficial but essential. Modern greenhouse operations integrate irrigation control with climate management systems, creating sophisticated growing environments that can achieve yields 10-20 times higher than open-field cultivation. The expansion of greenhouse vegetable production in regions like the Netherlands, Spain, and increasingly in Middle Eastern countries, drives continuous innovation in micro irrigation technology tailored to these intensive production systems.
Specialty crops, including herbs, spices, and medicinal plants, represent a rapidly growing niche within the agricultural segment. These high-value crops often require precise moisture management to optimize the concentration of essential oils or active compounds. Micro irrigation systems enable growers to manipulate plant stress strategically, enhancing product quality while conserving water. The cannabis industry, where legal, has emerged as a significant driver of advanced irrigation technology adoption, with growers investing in sophisticated fertigation systems that can deliver precise nutrient recipes to different plant stages.
Regional Market Analysis
Asia Pacific has emerged as the most dynamic region in the global micro irrigation systems market, driven by a combination of factors including massive agricultural sectors, increasing water scarcity, and supportive government policies. India alone accounts for the largest irrigated area globally, with ambitious targets to bring 10 million hectares under micro irrigation by 2030. The Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) program provides subsidies covering 55-75% of system costs, making micro irrigation accessible to small and marginal farmers. China’s modernization of its agricultural sector includes substantial investments in water-saving irrigation infrastructure, with particular focus on the water-stressed northern provinces.
The region’s growth is further accelerated by the increasing cultivation of high-value horticultural crops for both domestic consumption and export markets. Countries like Vietnam, Thailand, and the Philippines are rapidly adopting micro irrigation for crops like dragon fruit, durian, and high-value vegetables. The integration of Israeli and European technology with local manufacturing capabilities has created a competitive ecosystem that delivers cost-effective solutions tailored to regional needs. Climate variability, exemplified by increasingly erratic monsoon patterns, adds urgency to the adoption of reliable irrigation systems that can ensure crop survival during dry spells.
North America maintains its position as a mature but steadily growing market, with the United States and Mexico driving demand through different dynamics. In the United States, the depletion of aquifer resources, particularly the Ogallala Aquifer, forces farmers to maximize the value of every drop of water extracted. California’s Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA) has created a regulatory environment where micro irrigation becomes essential for agricultural survival. The integration of precision agriculture technologies, including variable rate irrigation and soil moisture sensing, positions North American farmers at the forefront of irrigation efficiency.
Europe, Middle East, and Africa present contrasting market dynamics within a single regional classification. European markets focus on technological sophistication and sustainability, with countries like Spain and Italy leading in greenhouse irrigation systems. The Middle East, despite limited agricultural area, invests heavily in advanced irrigation technology to achieve food security goals in arid environments. Africa represents the highest growth potential, with countries like Morocco, Egypt, and South Africa demonstrating successful large-scale adoption while sub-Saharan Africa begins to embrace micro irrigation through development programs and private sector initiatives.
Competitive Landscape
The micro irrigation systems market features a diverse competitive landscape where global technology leaders coexist with regional specialists and emerging innovators. Netafim, the Israeli pioneer of drip irrigation, maintains its market leadership through continuous innovation and a comprehensive product portfolio spanning from basic drip systems to advanced digital farming solutions. The company’s recent developments in digital irrigation management, including cloud-based monitoring and control systems, exemplify how traditional irrigation companies are transforming into agricultural technology providers.
Jain Irrigation Systems, based in India, has leveraged its understanding of emerging market dynamics to become a global force, particularly strong in Asia and Africa. The company’s integrated approach, combining irrigation equipment with agronomic support and tissue culture plants, creates a comprehensive ecosystem for farmers. Lindsay Corporation from the United States brings its expertise in center pivot irrigation to the micro irrigation space, offering hybrid solutions that combine the coverage of mechanical systems with the efficiency of micro irrigation.
Recent market developments reveal intensifying competition through technological differentiation rather than price alone. Companies are investing heavily in IoT integration, developing smart irrigation controllers that can process data from multiple sensors to optimize irrigation decisions. The acquisition trend continues, with larger agricultural companies acquiring specialized irrigation firms to complete their precision agriculture portfolios. For instance, recent acquisitions have seen traditional chemical and seed companies entering the irrigation space, recognizing water management as integral to their crop productivity solutions.
Strategic partnerships between irrigation companies and technology firms are reshaping the competitive dynamics. Collaborations with satellite imaging companies, weather data providers, and agricultural software platforms create comprehensive decision support systems that extend far beyond simple water delivery. Companies are also focusing on sustainability credentials, developing biodegradable drip tapes and recycling programs to address environmental concerns. The shift towards servitization, where companies offer irrigation-as-a-service models including design, installation, and maintenance, represents another competitive strategy particularly relevant in markets with limited technical expertise.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of micro irrigation systems is being shaped by the convergence of multiple technological advances that promise to revolutionize water management in agriculture. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are beginning to process vast amounts of field data to predict irrigation requirements with unprecedented accuracy. These systems can integrate weather forecasts, soil moisture data, plant growth stage information, and even market price projections to optimize not just water use but overall farm profitability. The development of self-learning algorithms that improve their predictions based on historical outcomes represents a paradigm shift from reactive to truly predictive irrigation management.
The integration of fertigation with precision irrigation systems continues to evolve, with new developments in nutrient sensors enabling real-time adjustment of fertilizer concentrations. Variable rate fertigation, where different zones within a field receive customized nutrient applications based on soil tests and yield maps, is becoming commercially viable. The development of organic-compatible fertigation solutions addresses the growing organic agriculture sector, while nano-technology promises to enhance nutrient uptake efficiency, potentially reducing fertilizer requirements by 30-50%.
Automation in micro irrigation is advancing rapidly, with fully autonomous systems that can detect and respond to leaks, adjust for weather changes, and even perform basic maintenance tasks. Robotic systems for irrigation installation and maintenance are under development, potentially addressing labor shortages and reducing installation costs. The integration of drone technology for system monitoring and thermal imaging for stress detection creates new possibilities for large-scale irrigation management with minimal human intervention.
Sustainability initiatives are driving innovation in materials and system design. Biodegradable drip tapes made from renewable resources are moving from laboratory to field trials, promising to address the plastic waste challenge. Solar-powered irrigation systems with integrated battery storage enable off-grid irrigation, particularly relevant for smallholder farmers in developing countries. Water treatment technologies, including advanced filtration and pathogen control systems, enable the safe use of recycled water and expand the potential water sources for irrigation. The development of closed-loop systems that capture and reuse drainage water represents the ultimate goal in irrigation efficiency, potentially achieving near-zero water waste in controlled environment agriculture.
☎ Contact Us:
224 W 35th St Ste 500 New York,
USA/Canada Toll Free +1(877) 462-2282
+1(212) 951-1369
✉ Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://www.vantagemarketresearch.com
FAQs
- What factors are driving the growth of the Global Micro Irrigation Systems market?
- How is artificial intelligence influencing Micro Irrigation Systems?
- What is the projected value of the Micro Irrigation Systems market by 2035?
- What role does efficient water resource management play in the Micro Irrigation Systems market?
![[Market Research Reports] – Research Google News Blog | VMR.Biz](https://www.vmr.biz/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/logo-removebg-preview.png)