Precision Farming: Revolutionizing Agriculture Through Technology and Innovation
Key Takeaways
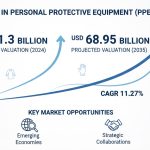
- The global precision farming market is experiencing explosive growth, valued at USD 8,709.18 million in 2022 and projected to reach USD 21,410.06 million by 2030, representing a CAGR of 11.90%
- IoT sensors, GPS technology, and advanced analytics are transforming traditional farming practices into data-driven operations
- North America currently dominates the market, but Asia-Pacific shows the highest growth potential due to increasing agricultural modernization
- Hardware solutions including guidance systems and variable rate technology lead market segments, while software and services show rapid expansion
- Major players like John Deere, Trimble, and AGCO Corporation are driving innovation through strategic partnerships and technological advancements
- High initial investment costs remain the primary barrier to adoption, particularly in developing nations
- Climate change mitigation and sustainable farming practices are becoming key drivers for precision farming adoption globally
Market Overview and Growth Trajectory
The Precision Farming Market stands at a pivotal moment in agricultural history, representing a fundamental shift in how food production meets the demands of a growing global population. With a current valuation of USD 8,709.18 million in 2022, the market’s trajectory toward USD 21,410.06 million by 2030 reflects not just growth, but a transformation in agricultural practices worldwide. This remarkable expansion, driven by a compound annual growth rate of 11.90%, underscores the increasing recognition of precision farming as essential rather than optional in modern agriculture.
The primary drivers fueling this market expansion are multifaceted and interconnected. Population growth continues to exert pressure on agricultural systems, with the global population expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, necessitating a 70% increase in food production. Simultaneously, arable land continues to decrease due to urbanization and environmental degradation, making efficiency improvements through precision farming not just beneficial but critical for food security. The convergence of these factors with advancing technology creates a perfect storm for market growth.
Geographical trends reveal distinct patterns in precision farming adoption. North America, particularly the United States and Canada, leads global implementation due to large-scale farming operations, technological infrastructure, and supportive government policies. Europe follows closely, driven by stringent environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives under the Common Agricultural Policy. However, the most dramatic growth occurs in Asia-Pacific, where countries like China and India are rapidly modernizing their agricultural sectors. Latin America and Africa, while currently smaller markets, show significant potential as infrastructure improves and awareness increases about precision farming benefits.
Technological Innovations Driving Precision Farming
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as the backbone of modern precision farming, creating interconnected networks of sensors, devices, and systems that continuously monitor and optimize agricultural operations. These IoT ecosystems collect vast amounts of data on soil moisture, nutrient levels, weather conditions, and crop health, transmitting information in real-time to centralized management systems. Advanced analytics platforms then process this data, employing machine learning algorithms to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and recommend optimal interventions. This integration of IoT and analytics transforms reactive farming into proactive management, enabling farmers to address issues before they impact yields.
GPS technology and remote sensing have revolutionized field management by providing unprecedented accuracy in agricultural operations. Modern GPS systems achieve sub-inch accuracy, enabling precise application of seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides, reducing waste and environmental impact. Satellite imagery and drone-based remote sensing complement GPS technology by providing comprehensive field monitoring capabilities. These technologies detect crop stress, identify pest infestations, and assess irrigation needs across vast areas, allowing farmers to make informed decisions based on actual field conditions rather than assumptions or generalizations.
Emerging technologies continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in precision farming. Autonomous tractors and robotic systems represent the next frontier, capable of operating continuously without human intervention while maintaining optimal precision. These machines integrate multiple technologies including computer vision, artificial intelligence, and advanced navigation systems to perform complex tasks like selective harvesting, targeted spraying, and precision planting. Additionally, blockchain technology is beginning to find applications in supply chain transparency and traceability, while augmented reality systems help farmers visualize data overlays on their fields, making complex information more accessible and actionable.
Key Market Segments and Applications
The precision farming market divides into distinct segments, with hardware solutions currently commanding the largest market share. Hardware offerings include guidance and steering systems, display devices, sensors, and variable rate technology equipment. These physical components form the foundation of precision farming operations, with GPS guidance systems alone accounting for a significant portion of hardware sales. However, the services segment shows the fastest growth rate, as farmers increasingly seek expertise in data interpretation, system integration, and ongoing support. Software solutions bridge hardware and services, providing the platforms necessary for data analysis, farm management, and decision support.
Main applications of precision farming technology vary by crop type and farming operation, but several key areas dominate market share. Variable rate application technology leads adoption rates, allowing farmers to apply inputs based on specific field conditions rather than uniform applications. Yield monitoring and mapping follow closely, providing crucial feedback on farming practices and enabling continuous improvement. Crop scouting applications, enhanced by drone technology and satellite imagery, help identify problems early and target interventions precisely. Irrigation management systems, particularly important in water-scarce regions, optimize water usage while maintaining or improving yields.
Soil monitoring and yield tracking represent critical components of precision farming success. Advanced soil sensors measure multiple parameters including moisture, temperature, pH, and nutrient levels at various depths, providing comprehensive soil health profiles. This data integrates with yield tracking systems that use combine-mounted sensors to create detailed yield maps. The correlation between soil conditions and yield outcomes enables farmers to identify cause-and-effect relationships, optimize input applications, and improve long-term soil health. These insights prove particularly valuable for implementing sustainable farming practices and meeting environmental regulations while maintaining profitability.
Competitive Landscape and Major Players
The precision farming market features a diverse competitive landscape with established agricultural equipment manufacturers, technology companies, and innovative startups vying for market share. Industry giants like John Deere, Trimble, and AGCO Corporation leverage their extensive dealer networks and brand recognition to maintain leading positions. These companies invest heavily in research and development, with John Deere alone spending over $1.5 billion annually on technology development. Their strategies focus on creating comprehensive ecosystems that integrate hardware, software, and services, making it convenient for farmers to adopt complete precision farming solutions.
Recent mergers, acquisitions, and collaborations reshape the competitive dynamics of the precision farming market. Major equipment manufacturers acquire technology startups to accelerate innovation and expand capabilities. For instance, CNH Industrial’s acquisition of Raven Industries for $2.1 billion demonstrates the value placed on precision technology. Strategic partnerships between traditional agricultural companies and technology firms become increasingly common, combining agricultural expertise with cutting-edge technology development. These collaborations often focus on specific challenges like data interoperability, creating industry standards that benefit all stakeholders.
Market leaders employ various strategies to capture and maintain market share in this rapidly evolving industry. Subscription-based service models gain traction, providing recurring revenue streams while making advanced technology more accessible to smaller farms. Companies invest in user education and training programs, recognizing that technology adoption depends on farmer confidence and competence. Additionally, leaders focus on developing region-specific solutions that address local agricultural challenges, climate conditions, and regulatory requirements. This localization strategy proves particularly effective in emerging markets where one-size-fits-all solutions often fail to gain traction.
Regional Analysis: Spotlight on Key Markets
North America’s dominance in the precision farming market stems from several converging factors that create an ideal environment for technology adoption. Large-scale farming operations in the United States and Canada provide economies of scale that justify significant technology investments. The region’s advanced technological infrastructure, including widespread broadband coverage and GPS availability, supports sophisticated precision farming applications. Government support through programs like the USDA’s Environmental Quality Incentives Program provides financial assistance for precision agriculture adoption. Current trends in North America include increasing integration of artificial intelligence, growing emphasis on sustainability metrics, and expansion of precision farming beyond row crops into specialty crops and livestock operations.
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing regional market for precision farming, driven by rapid agricultural modernization in countries like China, India, and Australia. China’s government actively promotes precision agriculture through subsidies and demonstration projects, recognizing its potential to address food security challenges. India’s growing startup ecosystem develops innovative solutions tailored to smallholder farmers, making precision farming accessible to previously underserved markets. Australia’s large-scale farming operations and variable climate conditions create strong demand for precision farming technologies. The region’s growth potential stems from its large agricultural sector, increasing technology adoption rates, and government support for agricultural modernization.
European precision farming adoption reflects the region’s focus on environmental sustainability and regulatory compliance. The European Union’s Common Agricultural Policy increasingly ties subsidies to environmental performance, incentivizing precision farming adoption. Countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands lead implementation, with high-tech greenhouse operations in the Netherlands serving as global models for precision agriculture. Factors influencing agricultural practices in Europe include strict environmental regulations, consumer demand for sustainable food production, and labor shortages driving automation adoption. The region’s emphasis on precision farming as a tool for environmental protection rather than just productivity enhancement creates unique market dynamics and opportunities.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
High implementation costs remain the most significant barrier to precision farming adoption, particularly for small and medium-sized farming operations. Initial investments in GPS systems, sensors, variable rate equipment, and software platforms can exceed hundreds of thousands of dollars for comprehensive implementations. While return on investment typically justifies these costs over time, the upfront capital requirements create substantial barriers. Additionally, ongoing costs for software subscriptions, data storage, equipment maintenance, and technical support add to the financial burden. Market awareness compounds this challenge, as many farmers lack understanding of precision farming benefits or struggle to quantify potential returns, making investment decisions difficult.
Technological barriers in developing nations present unique challenges that differ from those in developed markets. Limited internet connectivity in rural areas prevents real-time data transmission and cloud-based analytics. Inadequate GPS coverage or accuracy in some regions limits the effectiveness of guidance systems. The lack of technical support infrastructure means farmers cannot access help when systems malfunction or require updates. Educational barriers also play a role, as farmers may lack the technical skills needed to operate sophisticated equipment and interpret data effectively. These challenges require tailored solutions that consider local infrastructure limitations and farmer capabilities.
Climate change and environmental regulations create both challenges and opportunities for precision farming adoption. Increasing weather volatility makes traditional farming practices less reliable, driving demand for precision technologies that can adapt to changing conditions. However, extreme weather events can damage sensitive electronic equipment, requiring additional protection and redundancy. Environmental regulations increasingly require detailed documentation of input applications and environmental impacts, which precision farming systems can provide. Yet compliance with varying regional regulations complicates system design and implementation. The intersection of climate adaptation and regulatory compliance positions precision farming as essential for future agricultural sustainability, despite implementation challenges.
Future Outlook: Market Forecasts and Trends
Market projections through 2030 paint an optimistic picture for precision farming, with the anticipated value of USD 21,410.06 million representing just the beginning of a longer transformation. Growth rates are expected to accelerate in emerging markets as infrastructure improves and technology costs decrease. The integration of 5G networks will enable real-time data processing and control of autonomous equipment, opening new possibilities for precision and efficiency. Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications will become increasingly sophisticated, moving from descriptive analytics to prescriptive recommendations that consider multiple variables and optimize for various outcomes simultaneously.
Consumer behavior and market evolution will significantly influence precision farming development over the coming decade. Growing consumer awareness of food production methods drives demand for transparency and sustainability, which precision farming can provide through detailed tracking and reporting. The rise of carbon markets and sustainability certifications creates new revenue streams for farmers who can document reduced environmental impacts through precision farming practices. Market evolution will likely see increased consolidation as major players acquire innovative startups, while simultaneously, new entrants will continue to disrupt established practices with novel approaches and technologies.
Recommendations for stakeholders and investors in the precision farming field center on strategic positioning for long-term success. Investors should focus on companies developing interoperable solutions that work across different platforms and equipment brands, as data silos remain a significant challenge. Technologies that address specific regional challenges or crop types offer opportunities for differentiation and growth. Stakeholders should prioritize solutions that balance sophistication with usability, recognizing that farmer adoption depends on practical benefits and ease of use. Investment in education and support infrastructure will prove as important as technology development, as successful implementation requires knowledgeable users. Finally, stakeholders should consider the entire agricultural value chain, as precision farming’s benefits extend beyond the farm gate to food processors, retailers, and consumers.
☎ Contact Us:
224 W 35th St Ste 500 New York,
USA/Canada Toll Free +1(877) 462-2282
+1(212) 951-1369
✉ Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: https://www.vantagemarketresearch.com
FAQs
- What is the current value of the Global Precision Farming market?
- What factors are driving the growth of the Precision Farming market?
- What is the projected market value of Precision Farming by 2030?
- What is the expected CAGR for the Precision Farming market during the forecast period?
![[Market Research Reports] – Research Google News Blog | VMR.Biz](https://www.vmr.biz/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/logo-removebg-preview.png)